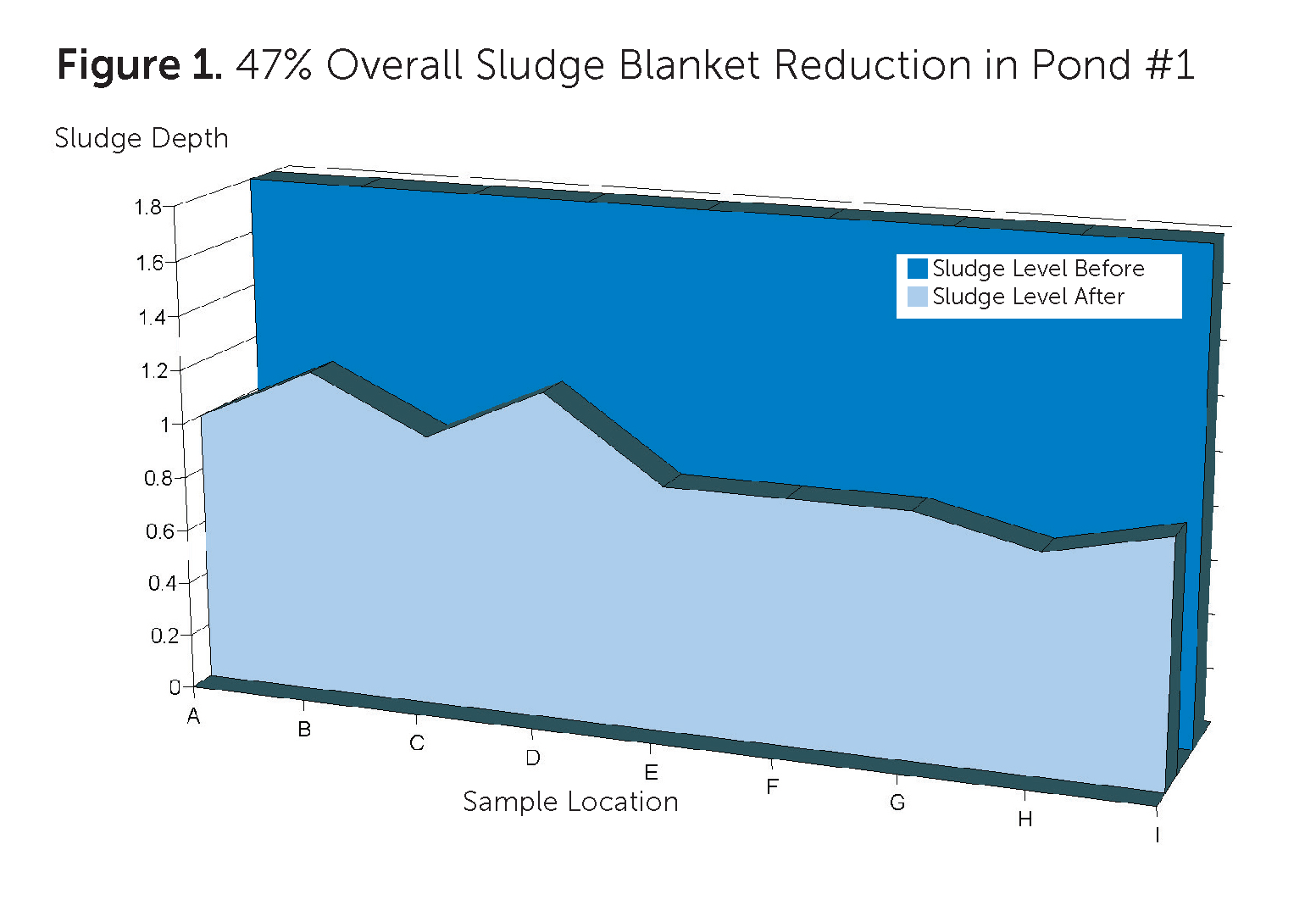
The wastewater treatment plant superintendent for a rural Colorado town of about 500 people noticed that the plant’s three wastewater lagoons were filling with sludge, but he was dealing with budget constraints. The town’s population fluctuates throughout the year, and the varied loading was affecting system performance. In addition, the aeration systems were not keeping up with the oxygen demand in the ponds. The superintendent decided to try a bioremediation approach to sludge reduction, using BIO ENERGIZER®, before embarking on the expensive process of mechanically dredging, hauling, and disposing of the sludge.
Using BIO ENERGIZER® is now saving the city thousands of dollars in mechanical dredging, hauling, and disposal costs. Lagoon desludging using BIO ENERGIZER® is typically one-fifth to one-tenth of the cost of mechanical dredging and land-applying or land-filling sludge.
Read the full report in English online
Read the full report in Spanish online
Download the full report in English
Download the full report in Spanish
Related Posts

Field Trial: X-Tend® Increases Glyphosate Effectiveness
Objective Over the years, some weeds have developed resistance to common herbicides such as glyphosate. To overcome this hurdle, growers may bump up the rates or add other herbicides or products with different mechanisms/modes of action into the tank mix. Such approaches have had mixed results over the long run and have increased the cost...

Microplex® JS Jump Starts Utah Summer Camp WWTF
by Heather Jennings, PE If I had to choose a favorite of our microbial products it would have to be our Microplex® JS product. It is a two-part formulation of a live synergistic blend of natural, Class I bacteria, specifically chosen for their ability to rapidly degrade solids, fats, lipids, proteins, detergents, hydrocarbons, and other...
Rural Colorado Town Uses BIO ENERGIZER® to Reduce Wastewater Lagoon Sludge and Save Money
The wastewater treatment plant superintendent for a rural Colorado town of about 500 people noticed that the plant’s three wastewater lagoons were filling with sludge, but he was dealing with budget constraints. The town’s population fluctuates throughout the year, and the varied loading was affecting system performance. In addition, the aeration systems were not keeping...