Virginia Tech Kentland Experimental Research Farm, McCoy, Va.
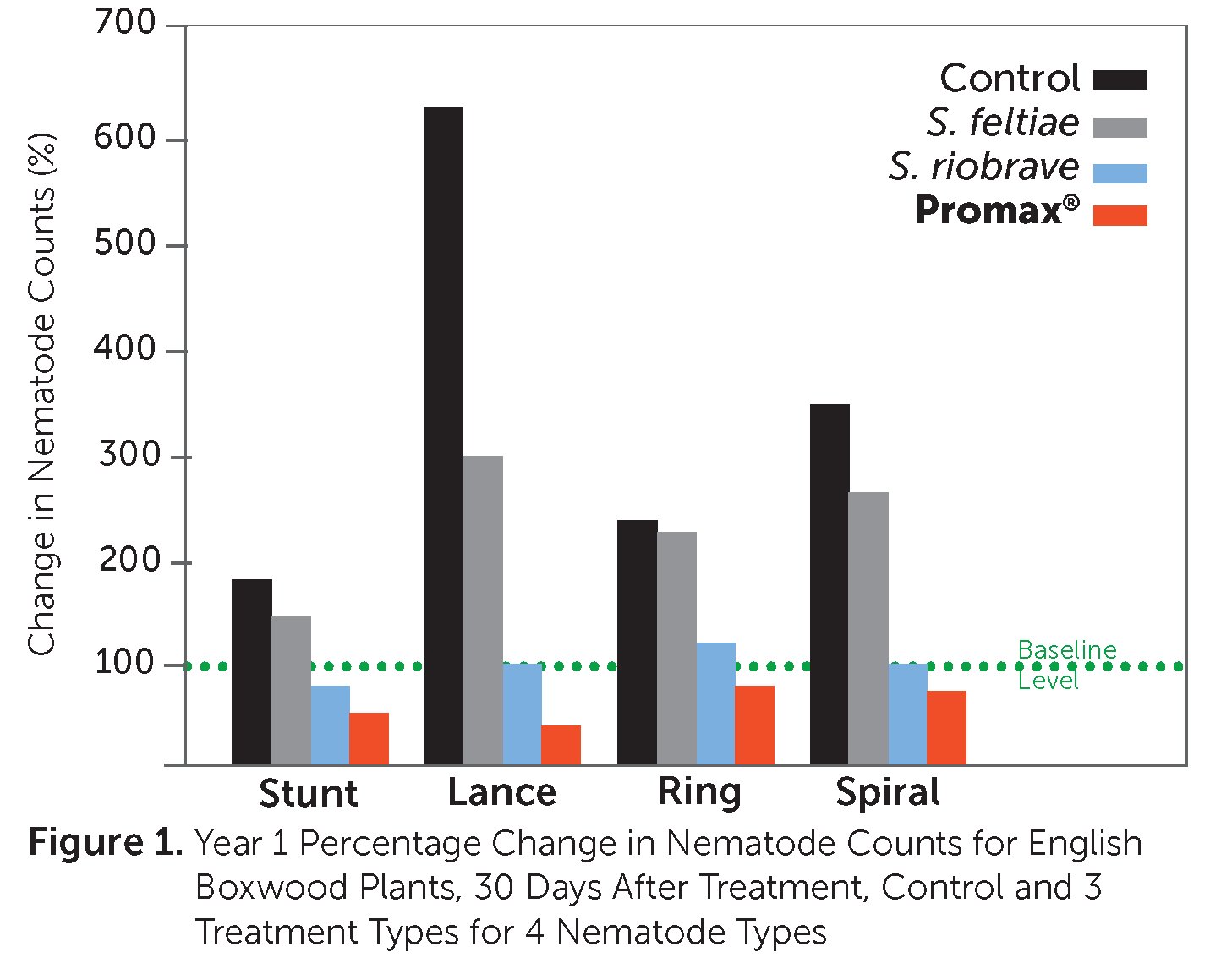
The results reported in this trial demonstrate that application of 1 treatment of the nematicide PROMAX® reduced population percentages of the 4 plant-parasitic nematodes studied at both 7 days and 30 days post-treatment in years 1 and 2, with PROMAX® being more effective than the other 2 treatments studied for both time periods. This is an indication that PROMAX® suppresses nematodes by killing them on contact.
Repeated applications may be required to achieve suppression for periods longer than 30 days.
Related Posts

Micronutrients Are the Key to Better Yields
Micronutrients play a critical role in plant vigor, yield, and harvest quality. Yet, they are often overlooked when growers develop their nutrient programs. In this article, we provide an overview of what micronutrients are, the roles they play, how availability is affected by soil and other conditions, how to recognize deficiencies, and the important steps to take when developing a micronutrient plan for your crops.

SUPER PHOS® and SUPER NITRO® Improve Spring Wheat Grain Yield and Quality
Research by Olga Walsh, PhD, University of Idaho The objectives of this study were (1) to compare the Micro Carbon Technology®-based phosphorus (P) product Super Phos® (SP) with traditional phosphorus (P) fertilizers ammonium polyphosphate (APP), and diammonium phosphate (DAP); and (2) to compare the Micro Carbon Technology®-based nitrogen (N) product Super Nitro® (SN) with the traditional nitrogen fertilizer, UAN. Huma Gro®

The Huma Gro Farmer Podcast: Episode 3 – Soil Biology and Soil Health with Zap®
In The Huma Gro Farmer podcast, Episode 3, we discuss Soil Biology and Soil Health with Zap®. Because a healthy soil biology is vital to a healthy crop, we must rebuild soil biology after fumigant or pesticide use. We discuss this with our experts, Bio Huma Netics, Inc. President and CEO Lyndon Smith, and Eastern U.S. Sales Manager and Agronomist Barrett Smith. Join us as we discuss how Zap® rebuilds soil biology after fumigant/pesticide use.

