Research by Brenda Tubana, PhD, Louisiana State University
The objective of this study was to compare, for use in Louisiana wheat production, the efficacy of a liquid silicon (Si) fertilizer (Huma Gro® Sili-Max®) with a commonly used dry Si source (steel slag) and another Si source (wollastonite) often used in research as a suspension. Silica deposition is an important barrier for foliar fungal diseases.
The wheat field study was conducted at Louisiana Ag-Center Research Stations. Silicon (Si) treatments were replicated four times and arranged in a randomized block design. There were 2 Huma Gro® Sili-Max® (10% Si) treatments (as a foliar band, and as foliar broadcast sprayed evenly over the entire plot). Each treatment was applied twice within 2 weeks at the onset of internode elongation (Feekes growth stage 5). The dry silicon sources (wollastonite [23% Si] and steel slag [11% Si]) were applied and incorporated into the soil prior to planting. Wheat leaf samples were collected one week after the application of silicon solution sources and evaluated for silica bodies (phytolith) deposition and percentage using scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive x-ray analysis.
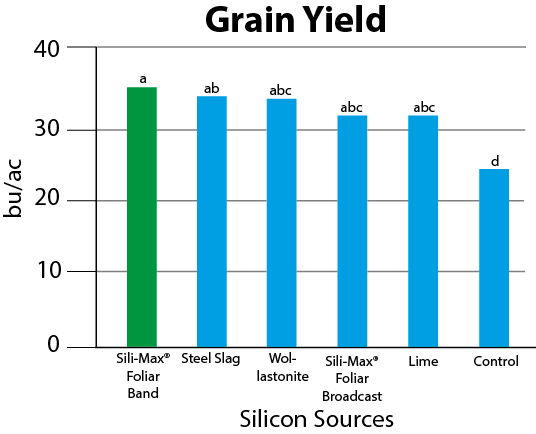
The accumulated silica bodies (phytolith) were 0.69% and 0.60% with Sili-Max® foliar broadcast and Sili-Max® foliar band treatments, respectively while the control had 0.53%.
Conclusions
Huma Gro® Sili-Max® applied as foliar band at a rate 3,900 times less than the dry silicon sources contributed to higher grain yield and straw yield, while the application of Sili-Max® as a foliar broadcast at a rate 1,900 times less than the dry silicon sources led to high Si deposition in wheat leaves.
Related Posts

Rye: A Popcorn Farmer’s Experience with Cover Crops
Nebraska farmer Dan Hilger recently incorporated rye into his corn and soybean crop rotation. Cover crops are a natural addition to Dan’s farming methods, which include minimum tillage and biostimulant inputs (Huma Gro® products). These practices increase soil health, reduce pest and weed pressure, and diversify his income.

HUMA GRO Training for Distributors and Clients from Peru and Mexico
Representatives from our distributors in México (Agroindustrias del Norte) and Perú (Agro Micro Bio Tech), along with some of their grape- and asparagus-producing clients (growers, farm managers, and technicians): The group spent two days at BHN headquarters in Gilbert, Arizona, receiving training in how to use HUMA GRO® products. BHN President and CEO Lyndon Smith...


