Location: Louisiana
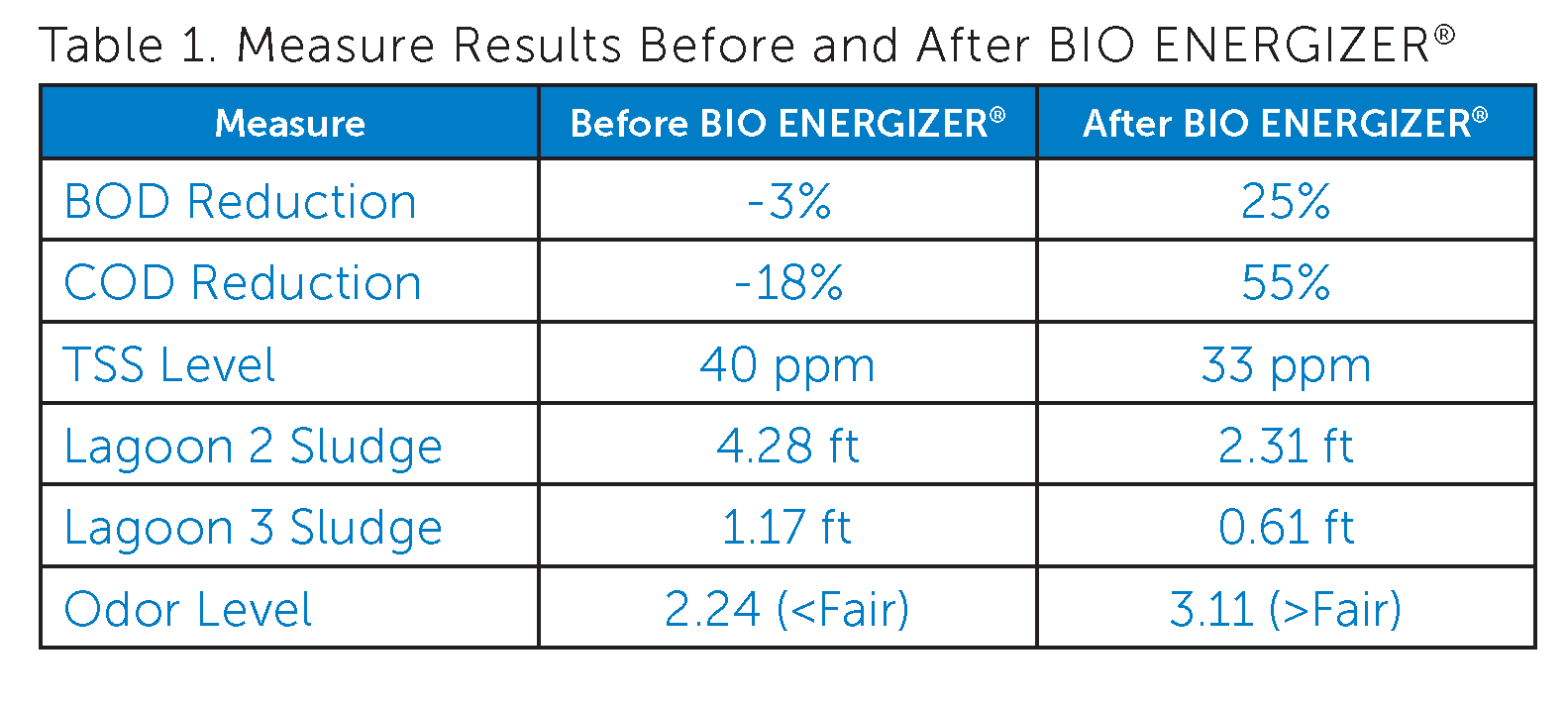
A large sugar refinery struggled with elevated BOD and COD values in its wastewater treatment lagoons due to the sugar refinery process. The lagoon wastewater system capacity was 25 million gallons with an influent of 1.25 million gallons per day. The wastewater system also suffered from accumulating sludge as well as significant odor issues. The sugar refinery had a history of periodically being unable to meet its National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permitting requirements.
Probiotic Solutions® BIO ENERGIZER® applied to a sugar refinery wastewater lagoon system over 9 months resulted in reduced accumulated sludge, TSS, and odors, with improved BOD and COD reduction.
Read the full report in English online
Read the full report in Spanish online
Download the full report PDF in English
Download the full report PDF in Spanish
Related Posts

Bio Energizer, Micatrol & Bio Feed Reduce COD and Stabilize Wastewater Treatment for Plastic Producer
A plastic manufacturer in Taiwan needed a new process to efficiently treat elevated incoming chemical oxygen demand (COD) to comply with stringent EPA regulations for effluent discharge. The plant is an activated sludge treatment system with an influent of approximately 2,000 cubic meters per day (CMD) which is equivalent to approximately 530,000 gallons per day

Video: Super Phos + Calcium Mixing Stability Test
English and Spanish subtitles are available. In this video, we demonstrate the unique compatibility of our highly concentrated Super Phos® 0-50-0 product when mixed with calcium. In traditional fertilizers, when phosphorus and calcium are mixed they can precipitate and fall out of solution. The resulting calcium phosphate can clog drip emitters and damage sprayers. Our
BIO ENERGIZER® Reduces Sludge, BOD, and Odor—City in Illinois
A small town in Illinois (pop. 3,500) had a municipal wastewater system that was in need of sludge removal. The sludge accumulation problem had become so problematic that the sludge was visible at the surface. The exposed sludge was causing an odor problem for the nearby residents. In addition, due to the high solids accumulation,