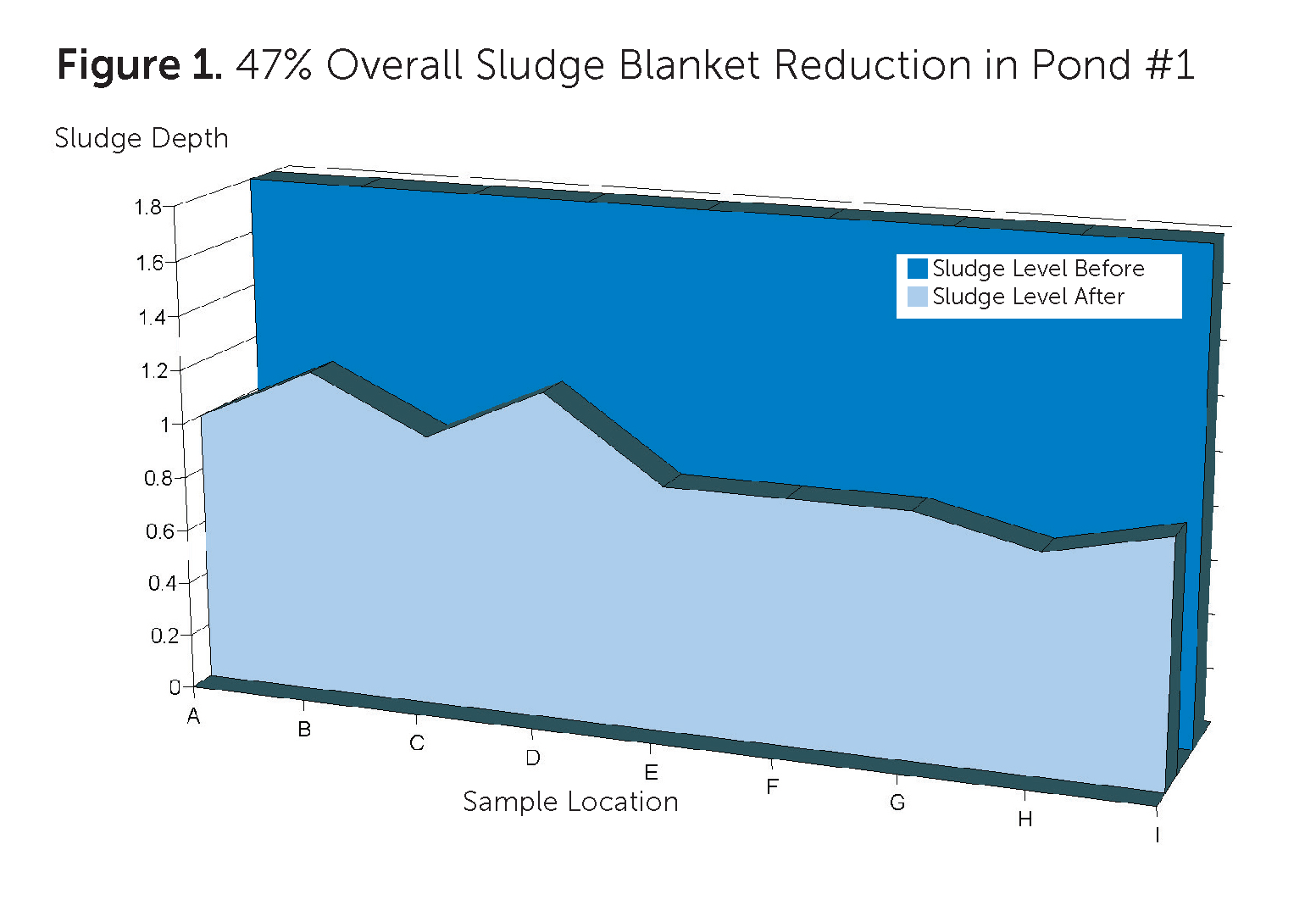
The wastewater treatment plant superintendent for a rural Colorado town of about 500 people noticed that the plant’s three wastewater lagoons were filling with sludge, but he was dealing with budget constraints. The town’s population fluctuates throughout the year, and the varied loading was affecting system performance. In addition, the aeration systems were not keeping up with the oxygen demand in the ponds. The superintendent decided to try a bioremediation approach to sludge reduction, using BIO ENERGIZER®, before embarking on the expensive process of mechanically dredging, hauling, and disposing of the sludge.
Using BIO ENERGIZER® is now saving the city thousands of dollars in mechanical dredging, hauling, and disposal costs. Lagoon desludging using BIO ENERGIZER® is typically one-fifth to one-tenth of the cost of mechanical dredging and land-applying or land-filling sludge.
Read the full report in English online
Read the full report in Spanish online
Download the full report in English
Download the full report in Spanish
Related Posts

PS Article Published in Tri-State Seminar Proceedings
An article by Heather Jennings, PE, Director of Probiotic Solutions®, has been published in Tri-State Seminars Magazine, the proceedings of the 36th Annual Tri-State Seminar, held on August 9–12, 2021, in Las Vegas, Nev. Ms. Jennings was a featured presenter at the seminar, which provides training and certification classes to educate water professionals from Arizona,

It’s ALIVE!
by Heather Jennings, PE . . . the lagoon sludge layer, that is. I’ve seen many lagoons full of sludge, and the general attitude I find in the water industry is that the sludge layer is inert and really can only be mechanically dredged. To a certain point, that is correct: sand, soil, grit, plastics—basically

Huma Gro® App Released for iOS Smart Phones
The Huma Gro® app for iOS smart phones has been released and is available for free at the Apple App Store. The Huma Gro® App provides a foliar application calculator for determining how much product to apply to specific crops on any size of field based on lab analysis, a continuously updated product document library,