TURFPLEX IV
Benefits of Use:
- More consistent and sustained turf color and texture
- Increased stress tolerance
- More efficient nutrient uptake without leaf burn
- Better stimulation of root growth in seedlings and transplants
Deficiency Symptoms—When to Apply:
- Plant stress caused by nutrient deficiencies, insects, disease, weather, chemicals, or mechanical damage
- Leaf symptoms: Yellow-to-brown leaf edge, pale green leaves, leaf tips dying
- Root symptoms: Shallow rooting
FAQs
Related Products
Related Case Studies

Humic Products Increase Soybean Yield In Iowa
Background Scientific research shows humic and fulvic acids can have a biostimulant effect on plant root growth and mass, nutrient availability and uptake, and crop yield and quality. Objective The objective of this study was to compare and contrast the immediate effects that three types of humic products from Huma®, Inc., have on soybean yield.

Recoverable Sugar of Sugar Beets Yield Increased Using Huma® Program, Year 2
Objective This field trial was conducted to observe effectiveness of additional preharvest applications of Huma® products on recoverable sugar of sugar beets and return on investment. Materials & Methods This trial on sugar beet (Beta vulgais vulg. altissima) was conducted in Homedale, Idaho. The crop was seeded on April 18 and was harvested on October

Huma® Promax® for Strawberries: A Replacement for Standard Fumigation, Nematicides, and Fungicides
Introduction A field trial to test efficacy of Huma® Promax® as a cropprotection product for strawberries (Fragaria sp.) was applied in a location known to have spring disease problems with either Fusarium or Macrophomina pathogenic fungi. This report is based on a field trial with strawberries conducted by Holden Agricultural Research and Consulting submitted on
Related Blog Posts

New Fertilgold® Organics Promo Video
There’s tremendous power in nature. What if you could harness that power and put nature’s science to work growing your premium organic crop? To see how, watch this 30-second introductory video for Fertilgold® Organics.
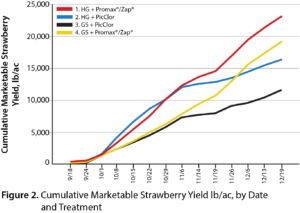
Huma Gro® Nutrient and Fumigation Replacement Program Increases Strawberry Yields 97%
Conducted by: Pacific Ag Research Huma Gro® Products: Ultra-Precision™ Blend (Fresca CA Strawberry Mix), Promax®, and Zap® OBJECTIVE This field trial assessed the effects on strawberry yields of replacing field fumigation with periodic applications of Huma Gro® Promax® and Zap® and replacing a grower’s standard fertilizer program with irrigation-applied Ultra-Precision™ blended liquid Huma Gro® crop










